Solidigm™ D5-P4326 Product Brief
Formerly Intel® SSD D5-P4326
Store more. Save more. Do more.
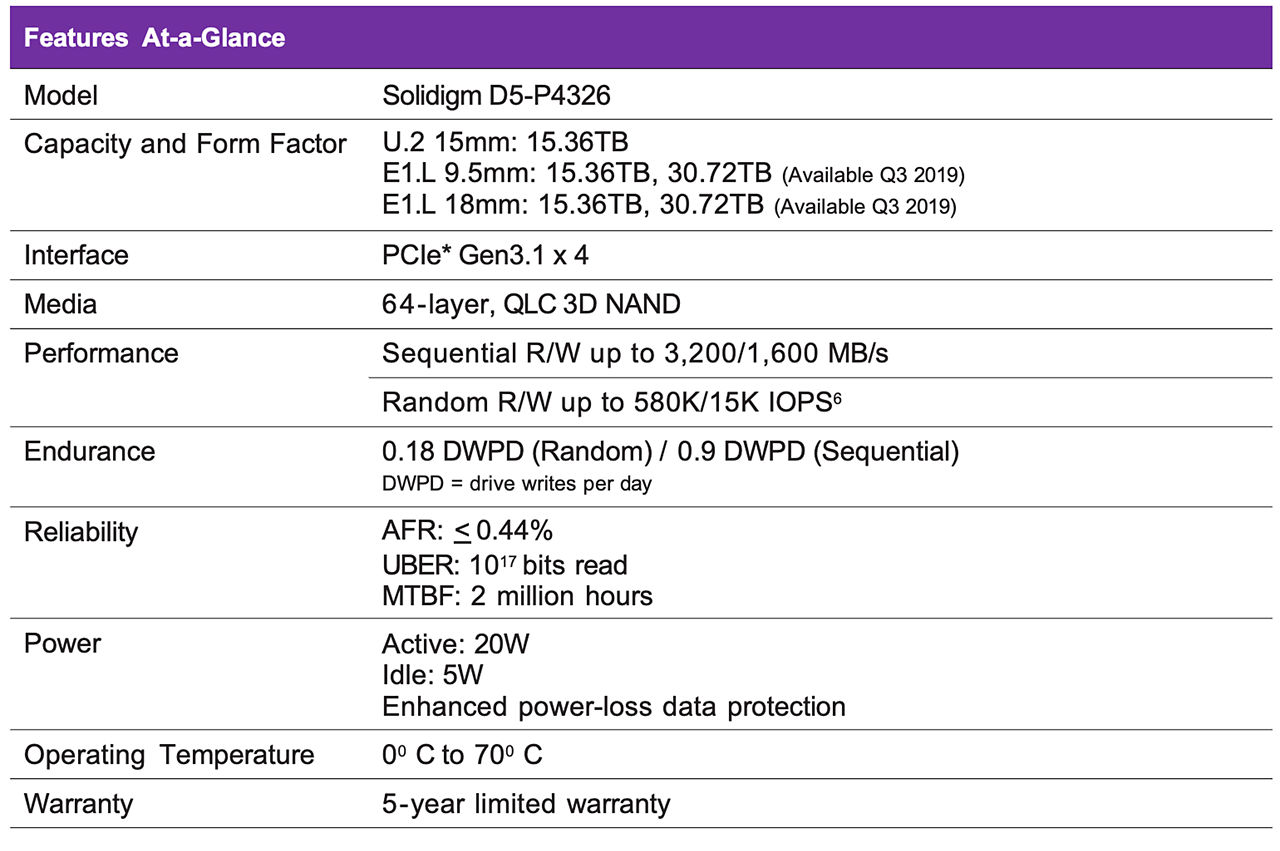
The Solidigm D5-P4326 SSD offers Solidigm QLC technology, PCIe* performance and the flexibility to scale solutions, maximize capacity, and improve operational efficiency at scale. In addition to a U.2 form factor, the Solidigm D5-P4326 is also the industry’s first SSD in the innovative E1.L form factor to offer Solidigm QLC technology based on EDSFF*.

The Solidigm SSD D5-P4326 includes Solidigm QLC’s 33% more bits per cell than prior generation Solidigm 3D NAND drives, [1] consolidating data center storage footprint up to 20x. [2] In addition to capacity, replacing HDDs with Solidigm QLC SSDs reduces power, cooling and drive replacement costs. [3] Thanks to the PCIe-based design, performance also gets a boost over SATA drives, allowing greater usable capacity meeting IOPS/TB requirements. [4]
Store more: Large capacity in a small space
The D5-P4326 with Solidigm QLC technology was designed to optimize per drive capacity with initial capacity at 15.36TB and future scaling to 30.72TB later in 2019. And, when delivered on the first-in-industry E1.L form factor, the D5-P4326 takes storage efficiency to another level with initial chassis designs supporting up to 32 drives in a 1U server. The combination of per drive and per rack capacity efficiency provides up to 10x storage consolidation compared to 8TB U.2 SSDs and up to 20x consolidation compared to 4TB HDDs. In fact, with E1.L-based chassis designs up to 36 drives possible, the D5-P4326 can scale to 1PB in 1U.
Save more: Innovations delivering operational efficiency
The D5-P4326 is a cost optimized addition to Solidigm’s QLC family. This affordability makes the D5-P4326 ideally suited to displace hard discs in all-HDD arrays and hybrid arrays. In addition to storage consolidation noted in the previous section, data centers choosing to displace their HDDs can lower power cost, reduce cooling cost and significantly save on drive replacement cost. When delivered on the operationally efficient E1.L form factor, data centers can realize even more cooling savings with the thermally optimized design and improve manageability and serviceability at scale with capabilities such as LED status lights, drive specific power cycling and opportunities to reduce component count.
Do more: PCIe accelerates workloads at large capacities
The IOPS of a drive is a fixed number meaning that as a drives capacity gets larger IOPS/TB get smaller. This can be problematic with certain storage workloads that have minimum IOPS/TB requirements. The performance advantage of the PCIe interface vs. SATA interface means IOPS/TB remain sufficiently high even as capacities scale.
Backed by Solidigm experience and innovation
Solidigm brings longstanding expertise and disruptive innovation in data management to address the capacity and performance issues of today’s data centers. Prepare for the future with PCIe Solidigm QLC SSDs, backed by Solidigm’s technology and manufacturing leadership.
What is EDSFF?
The Enterprise and Datacenter SSD Form Factor, created by a workgroup of 15 industry leaders to address data center storage concerns and define industry standard form factors, driven by three guiding principles:
- enable scale
- optimize total cost of ownership
- enable dynamic range of solutions
Notes
[1] Source: Solidigm. 33% more bits per cell. TLC (tri-level cell) contains 3 bits per cell and QLC (quad level cell) contains 4 bits per cell. Calculated as (4-3)/3 = 33% more bits per cell.
[2] Source: Solidigm. Consolidate storage footprints up to 20x. Comparing 3.5’ 4TB WD Gold TB Enterprise class 7200 RPM HDD enabling up 24 HDDs per 2U to 30.72TB E1.L Solidigm D5-P4326 (available at a future date) enabling up to 32 per 1U.
[3] 2U (1971W total power) https://www.seagate.com/files/www-content/datasheets/pdfs/exos-7-e8-data-sheet-DS1957-1-1709US-en_US.pdf SSD: 22W active power 44% AFR, 32 drives in 1U (704W total power); Cooling cost based on deployment term of 5 years with Kwh cost of $.158 and number of watts to cool 1 watt 1.20 Based on 3.5” HDD 2U 24 drives and EDSFF 1U Long 1U 32 drives. Hybrid storage based off using Solidigm TLC SSD for cache. Drive Replacement cost savings. Calculation: HDD 2% AFR x 256 drives x 5 years = 25.6 replacements in 5 years; SSD: 0.44% AFR x 32 drives x 5 years = 0.7 replacements in 5 years
[4] Source: NetApp. Scale usable capacity. Usable capacity is defined as any drive capacity that can provide up to 10K random 4K read IOPS/TB no matter how much total capacity the drive has. This was based on NetApp blog (https://blog.netapp.com/blogs/the-importance-of-io-density-in-delivering-storage-as-a-service-part-1/), which identifies ~8K IOPS/TB as the “extreme” workload threshold.
[5] Solidigm D5-P4326 uses 16KB Indirection Unit (IU). Solidigm recommends the write size to be aligned with the IU size. Please contact your Solidigm representative for details on how to optimize the performance and endurance on coarse IUSSD.
Software and workloads used in performance tests may have been optimized for performance only on Intel microprocessors. Performance tests, such as SYSmark and MobileMark, are measured using specific computer systems, components, software, operations and functions. Any change to any of those factors may cause the results to vary. You should consult other information and performance tests to assist you in fully evaluating your contemplated purchases, including the performance of that product when combined with other products. For more complete information visit https://www.solidigm.com/products/data-center/d5/p4326.html#interface
Solidigm features and benefits depend on system configuration and may require enabled hardware, software or service activation. Performance varies depending on system configuration. Check with your system manufacturer or retailer or learn more at solidigm.com.
Cost reduction scenarios described are intended as examples of how a given Solidigm-based product, in the specified circumstances and configurations, may affect future costs and provide cost savings. Circumstances will vary. Solidigm does not guarantee any costs or cost reduction.
Solidigm and the Solidigm logo are trademarks of Solidigm Technolgoy in the U.S. and/or other countries.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
© Solidigm Corporation