A CSAL-Based Reference Storage Platform
Open-source building blocks used for storage solutions are a complex mix of parts that are challenging to assemble and use. This complexity often hampers the rapid development, assessment, and deployment of these solutions. To overcome this problem, Solidigm has developed a reference storage platform in collaboration with Intel, StarWind, other industry partners, and the Storage Performance Development Kit (SPDK) community. This platform will help foster industry-wide collaboration and enable easy evaluation and adoption of technologies, such as data placement technologies (for example, Zoned Namespaces [ZNS] and Flexible Data Placement [FDP]), that are currently under development.

The reference platform uses commodity servers that are paired with an open-source software stack composed of SPDK and a Cloud Storage Acceleration Layer (CSAL) as the host-based flash translation layer (FTL). This solution brief discusses how Solidigm used this reference platform to demonstrate the unprecedented total cost of ownership (TCO) benefits of high-density storage from the newly released Solidigm™ D5-P5336 61.44 TB quad-level cell (QLC) SSD.
Benefits of the reference storage platform
The reference storage platform is an open, extensible, high-performance platform that enables hardware and software vendors to rapidly innovate (using high-density QLC, infrastructure processing units [IPUs], and data placement technologies, among other technologies). In addition, the platform enables system integrators and end customers to evaluate and adopt these innovations seamlessly in a fully implemented solution interface. Platform vendors and independent software vendors (ISVs) can extend the capability of the open-source platform with value-added innovations to create their own proprietary appliances and solutions.
What can CSAL accomplish?
The CSAL host-based FTL extends the use of Solidigm high-density QLC SSDs to mixed workloads. CSAL achieves this through the following four core capabilities:
1. Write shaping to enable a reduced SSD/DRAM footprint
Solidigm hyper-dense SSDs can help reduce DRAM costs while maintaining TLC read performance. CSAL shapes writes for emerging data placement interfaces that match the indirection unit (IU) size, bringing TCO advantages to mixed workloads.
2. Pooling to increase capacity and performance utilization
CSAL enables the sharing of large SSDs among multiple cloud applications/tenants, thereby increasing capacity and performance utilization.
3. RAID to enhance data protection and reliability
Under development in CSAL is a full-stripe RAID5 implementation that is 2x more efficient than traditional RAID5 in improving data protection and reliability.i
4. Reducing write amplification in multi-tenant environments
Mixed data placement can cause excessive write amplification in multi-tenant cloud environments. Under development in CSAL is the integration of data placement technologies. By optimizing data placement, aggregating writes, and scheduling input/output (I/O) operations, CSAL helps achieve true multi-tenant isolation and helps improve QLC performance and endurance.
Testing the platform with Solidigm QLC SSDs
Improved density has led to a significant TCO advantage. For example, by replacing HDD-based big data local disk instance 2nd generation (D2C) local-disk storage nodes with the Solidigm D5-P5316 QLC SSDs in their big data local disk instance 3rd generation nodes, Alibaba saw twice the performance and density over D2C.ii The D5-P5336 61.44 TB QLC SSD continued this trend by delivering 4x the density of the D5-P5316, with a 2x TCO reduction through lower capital expenditures (CapEx), smaller data center footprint, and subsequently less demand for maintenance personnel and associated equipment, cabling, and power. [1]1
Test configuration
To objectively evaluate its new highest density QLC SSDs using the reference platform, Solidigm compared a system with 10 Solidigm TLC drives without CSAL versus a 3 SLC + 7 QLC configuration using CSAL (this configuration used three 800 GB Solidigm first-generation SLC SSDs and seven 61.44 TB D5-P5336 SSDs as the capacity tier). Solidigm used a 4K 70/30 read/write workload to drive 80 percent utilization of the 100 Gbps network. CSAL utilizes SLC SSDs as a cache/write buffer, enabling efficient shaping of write workloads into sequential writes (see Figure 1).
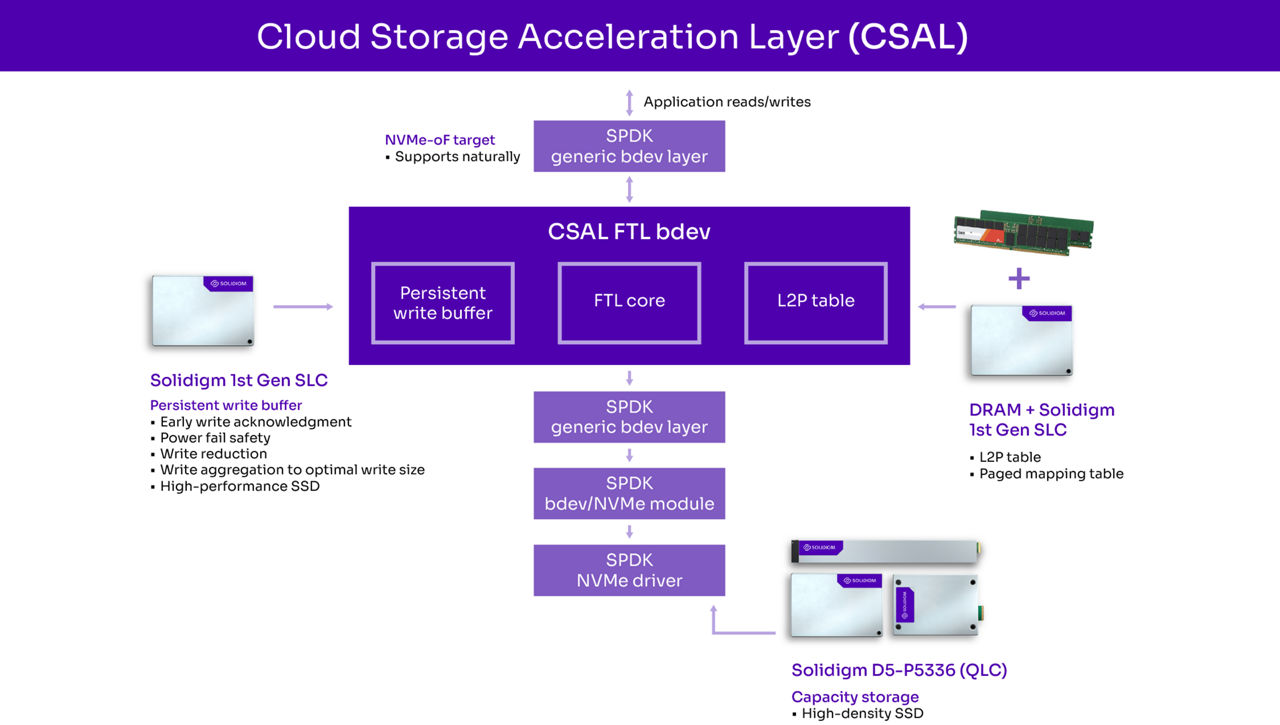
Figure 1. CSAL architecture
Both configurations were able to achieve the desired network saturation. While the TLC SSDs can deliver higher raw performance, the network bottleneck leaves the surplus bandwidth unutilized, which essentially led to both configurations delivering the same performance (see Table 1).
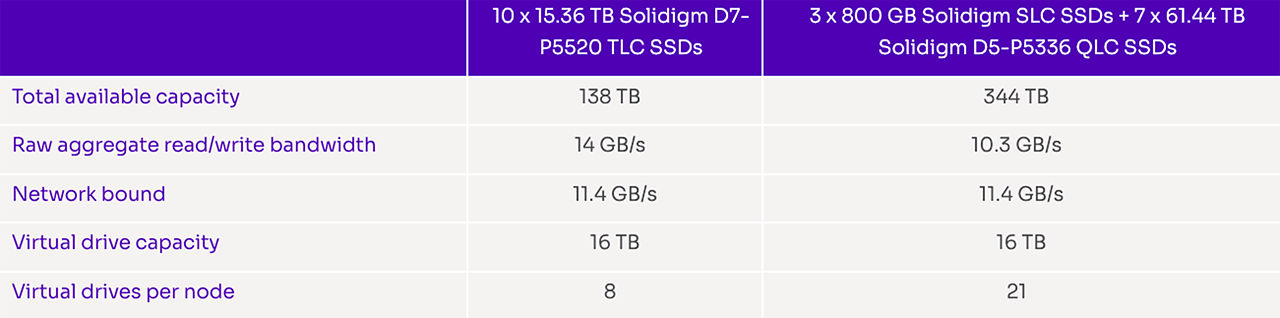
Table 1. CSAL test results comparison
Solidigm developed an internal model to quantify the TCO advantage of D5-P5336 QLC SSD density. A high-level comparison in Table 2 shows that the D5-P5336 QLC SSD can deliver the same performance at 35% lower TCO than the TLC configuration.
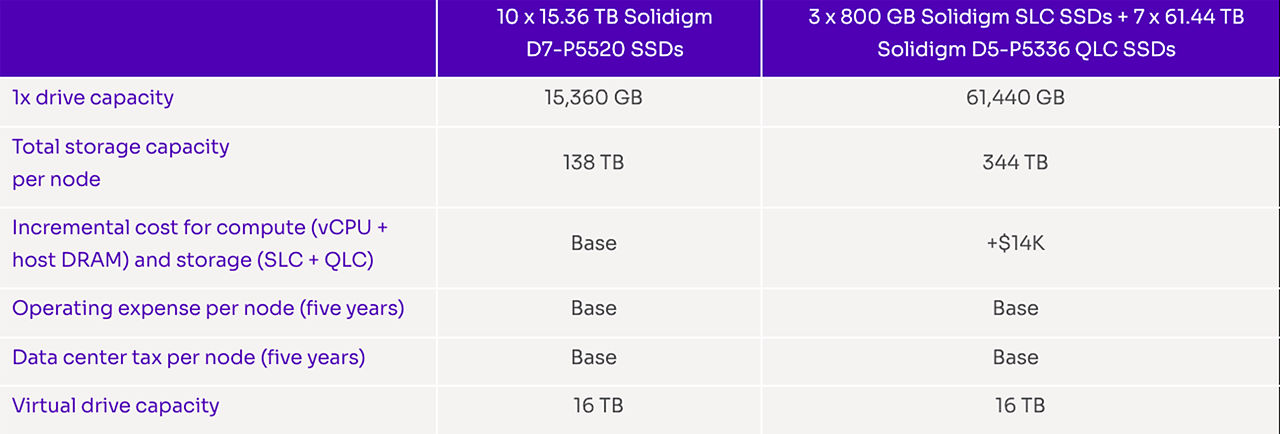
Table 2. CSAL TCO comparison
Solidigm invites platform vendors and end users to use the reference storage platform in their appliance and solution implementations. Innovators across the storage industry can use the reference platform and build upon it, ensuring a robust platform to showcase, evaluate, and accelerate the adoption of new storage solutions.
Try the reference storage platform today:
For reference, read the white paper, “Achieving Optimal Performance and Endurance on Course IU SSDs.”
[1] Based on Solidigm internal analysis.
[2] Intel. “A Media-Aware Cloud Storage Acceleration Layer (CSAL) Cache Solution with Intel® Optane™ SSDs for Alibaba ECS Local Disk D3C Service.” January 2023. www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/content-details/765062/a-media-aware-cloud-storage-acceleration-layer-csal-cache-solution-with-intel-optane-ssds-for-alibabaecs-local-disk-d3c-service.html.
Note: The Solidigm D5-P5316 is part of the storage configuration on the Intel platform discussed in this paper.
Solidigm technologies may require enabled hardware, software or service activation. No product or component can be absolutely secure. Your costs and results may vary. Performance varies by use, configuration and other factors. Other names and brands may be claimed as property of others. See our complete legal Notices and Disclaimers. Solidigm is committed to respecting human rights and avoiding complicity in human rights abuses. Solidigm products and software are intended only to be used in applications that do not cause or contribute to a violation of an internationally recognized human right. Solidigm does not control or audit third-party data. You should consult other sources to evaluate accuracy.
Solidigm and the Solidigm logo are trademarks of Solidigm. Intel is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
© Solidigm 2023. All rights reserved.